Solar Energy: Guide to unlock the Power of Sun
Are you ready to tap into the limitless energy of the sun? Picture a world where electricity flows effortlessly from the sky, fueling our homes, businesses, and communities with clean, renewable power. But how exactly does solar energy work, and why is it poised to revolutionize our future? Embark on a journey with us as we demystify the wonders of solar energy. From sleek rooftop panels to sprawling solar farms, there’s a universe of possibilities waiting to be explored. So, are you ready to take the plunge and unleash the potential of the sun?
In this ultimate guide, we’ll dive deep into the realm of solar energy, uncovering its myriad applications, advantages, and cutting-edge innovations. Prepare to be inspired, educated, and empowered to join the solar revolution. Let’s illuminate the path to a brighter, cleaner future together!
Types of Solar Technologies
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
PV systems, commonly known as solar panels, convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic cells. These cells are typically made of semiconductor materials such as silicon, which generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight. PV systems are versatile and can be used for both residential and commercial purposes, ranging from rooftop installations to large-scale solar farms.
Solar Thermal Systems
Solar thermal systems harness sunlight to produce heat, which can be used for various applications such as water heating, space heating, and industrial processes.

Unlike PV systems, which directly convert sunlight into electricity, solar thermal systems capture and utilize solar radiation to heat a fluid, typically water or air, which is then used to transfer heat energy.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
CSP technology utilizes mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, creating intense heat that can be used to generate electricity. This concentrated solar energy is often used to heat a fluid, such as molten salt or water, which then produces steam to drive a turbine generator. CSP plants are typically large-scale installations located in regions with high solar irradiance.
Applications of Solar Energy
Residential Solar Solutions
Residential solar solutions include rooftop solar panels, solar water heaters, and solar-powered appliances. These systems allow homeowners to generate their own electricity, reduce their reliance on grid power, and lower their utility bills. In addition to cost savings, residential solar installations also contribute to reducing carbon emissions and promoting environmental sustainability.
Commercial and Industrial Use
Commercial and industrial sectors utilize solar energy for a wide range of applications, including powering manufacturing processes, heating water for commercial buildings, and providing electricity for large-scale operations. Solar energy can help businesses reduce operating costs, enhance energy security, and demonstrate environmental leadership by reducing their carbon footprint.
Off-Grid Solar Solutions
Off-grid solar solutions are used in remote locations where access to grid power is limited or unavailable. These systems typically include solar panels, batteries for energy storage, and inverters for converting DC power to AC power. Off-grid solar solutions are commonly used for powering remote cabins, RVs, boats, and telecommunications equipment, providing reliable electricity in off-grid environments.
Benefits of Solar Energy
Environmental Benefits
Solar energy offers significant environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and dependence on fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of the sun, solar energy helps mitigate climate change, preserve natural resources, and protect ecosystems.
Economic Benefits
Solar energy provides economic benefits at both the individual and societal levels. For homeowners and businesses, solar installations offer long-term cost savings on electricity bills and increase property value. At the societal level, solar energy creates jobs, stimulates economic growth, and reduces reliance on imported energy sources.
Social Benefits
Solar energy promotes energy independence, energy security, and access to clean and affordable electricity for all. By democratizing energy production and distribution, solar energy empowers communities, reduces energy poverty, and improves quality of life for people around the world.
Factors Affecting Solar Energy Production
Solar Irradiance and Insolation
Solar irradiance refers to the amount of sunlight received at a specific location over a given period of time, typically measured in watts per square meter.
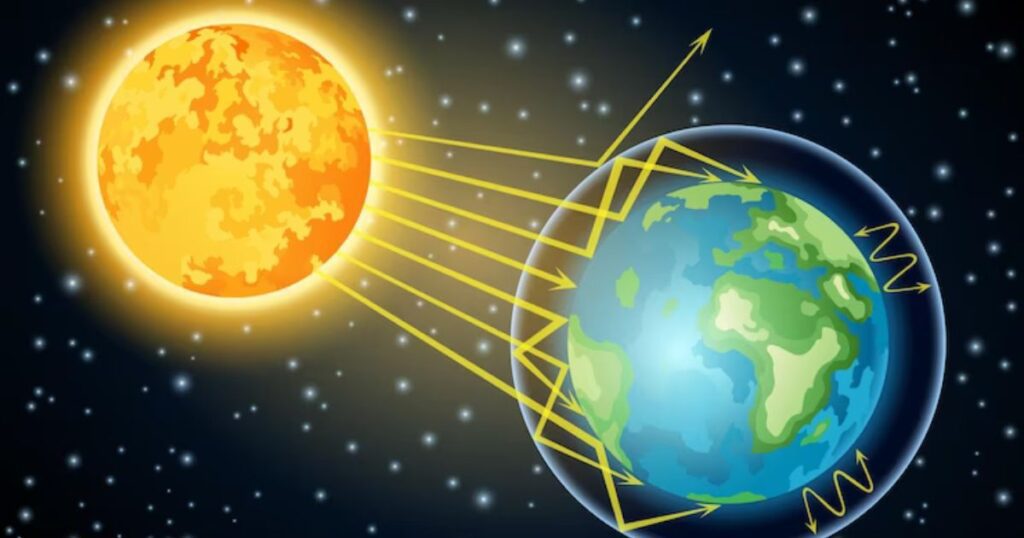
Insolation is the amount of solar radiation received on a horizontal surface, accounting for factors such as time of day, season, and weather conditions.
Geographic Location and Climate
Geographic location and climate play a significant role in determining the solar energy potential of a given area. Regions closer to the equator receive more sunlight throughout the year and generally have higher solar energy production potential compared to regions farther from the equator or with less sunlight exposure.
System Orientation and Tilt
The orientation and tilt angle of solar panels affect their efficiency and energy production. Ideally, solar panels should be oriented to face south (in the northern hemisphere) or north (in the southern hemisphere) to maximize sunlight exposure. Additionally, adjusting the tilt angle of solar panels according to the latitude of the location can optimize energy production throughout the year.
Components of Solar Energy Systems
Solar Panels
Solar panels consist of multiple photovoltaic cells interconnected to form a solar module. These cells convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, generating direct current (DC) electricity that can be used to power electrical devices or stored in batteries for later use.
Inverters
Inverters are essential components of solar energy systems that convert DC electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for use in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Inverters also optimize the performance of solar panels by maximizing power output and ensuring compatibility with the electrical grid.
Mounting Structures
Mounting structures, such as roof mounts, ground mounts, and tracking systems, support and secure solar panels in place. These structures are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including wind, snow, and seismic activity, while optimizing the orientation and tilt angle of solar panels for maximum energy production.
Solar Energy Policy and Regulation
Government Incentives and Rebates
Many governments offer financial incentives, tax credits, and rebates to promote the adoption of solar-energy. These incentives can include investment tax credits, production-based incentives, feed-in tariffs, and property tax exemptions, making solar-energy more affordable and accessible to homeowners, businesses, and utilities.
Net Metering Policies
Net metering allows solar-energy system owners to receive credit for excess electricity generated by their systems and exported to the grid. Under net metering policies, utilities compensate solar-energy producers for the surplus energy they contribute to the grid, effectively reducing electricity bills and promoting grid stability and reliability.
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs), also known as green certificates or tradable renewable credits, represent the environmental attributes of renewable energy generation, including solar-energy. RECs can be bought, sold, or traded on the open market, allowing businesses and organizations to support renewable energy projects and meet sustainability goals.
Solar Energy Financing Options
Purchase Options (Cash, Loan, Lease)
Solar-energy systems can be purchased outright with cash, financed through a solar loan, or leased through a solar lease or power purchase agreement (PPA). Cash purchases offer the greatest long-term savings, while solar loans and leases provide affordable financing options with little to no upfront costs.
Solar Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
Solar Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) allow homeowners and businesses to purchase solar-energy generated by a third-party provider at a predetermined rate over a fixed term. PPAs typically require little to no upfront investment and offer predictable electricity costs, making solar-energy more accessible and affordable for consumers.
Community Solar Programs
Community solar programs enable multiple individuals or organizations to share ownership of a solar-energy system located off-site, such as on a community-owned solar farm or shared rooftop installation. Participants receive credits or discounts on their electricity bills based on their share of the solar-energy produced, regardless of whether the solar panels are located on their property.
Maintenance and Care of Solar Energy Systems
Cleaning and Inspection
Regular cleaning and inspection of solar panels are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of solar-energy systems. Dust, dirt, debris, and bird droppings can accumulate on solar panels over time, reducing their efficiency and energy production. Periodic cleaning and inspection help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues that may affect solar-energy systems include shading, soiling, module degradation, and electrical faults. Shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce solar panel efficiency, while soiling from dust, pollen, or bird droppings can create hot spots and decrease energy production. Module degradation and electrical faults require prompt diagnosis and repair to prevent further damage and ensure system reliability.
Professional Maintenance Services
Professional maintenance services, provided by certified solar installers or technicians, offer comprehensive cleaning, inspection, and maintenance of solar energy systems. These services typically include routine maintenance checks, performance monitoring, and warranty support to ensure optimal system performance, maximize energy production, and prolong the lifespan of solar panels and components.
Environmental Impact of Solar Energy
Life Cycle Analysis
Life cycle analysis (LCA) evaluates the environmental impacts of solar-energy systems from production to disposal, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, installation, operation, and end-of-life disposal or recycling. LCA helps assess the overall environmental footprint of solar-energy compared to conventional energy sources and identifies opportunities for improvement in manufacturing processes, materials sourcing, and end-of-life management.
Land Use and Habitat Impact
The land use and habitat impact of solar-energy systems vary depending on factors such as installation scale, location, and land management practices. Large-scale solar installations, such as solar farms or utility-scale CSP plants, may require significant land area and have the potential to impact local ecosystems, habitats, and biodiversity. Proper siting, land use planning, and environmental mitigation measures are essential to minimize land use conflicts and habitat degradation associated with solar-energy development.
Recycling and Disposal of Solar Components
The recycling and disposal of solar components, including solar panels, inverters, and mounting structures, are critical considerations for managing the end-of-life impacts of solar-energy systems. Solar panels contain valuable materials such as glass, aluminum, and silicon, which can be recycled and reused in new manufacturing processes. Proper recycling and disposal practices ensure the recovery of valuable resources, reduce waste, and minimize environmental pollution associated with solar-energy production.
Emerging Trends in Solar Energy
Solar Energy Storage Technologies
Solar energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, enable the storage of excess solar-energy generated during periods of high sunlight for use during periods of low sunlight or high energy demand. Advances in battery technology, including lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and solid-state batteries, are driving innovation in solar-energy storage solutions, enhancing grid stability, and enabling greater integration of renewable energy sources.
Solar Integration with Smart Grids
The integration of solar-energy with smart grid technologies enables more efficient, reliable, and resilient electricity delivery and management. Smart grid technologies, including advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), distribution automation, and demand response systems, enable real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of electricity generation, transmission, and distribution, facilitating greater penetration of solar-energy and other renewable energy sources into the grid.
Advances in Solar Panel Efficiency
Advances in solar panel efficiency, manufacturing processes, and materials are driving down the cost of solar-energy and increasing its competitiveness with conventional energy sources. Emerging technologies such as perovskite solar cells, tandem solar cells, and bifacial solar panels offer higher efficiency, lower production costs, and improved performance in low-light conditions, further expanding the potential applications and benefits of solar-energy worldwide.
By exploring these topics in-depth, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of solar-energy and its various applications, benefits, challenges, and emerging trends. Whether you’re a homeowner considering solar panels for your roof, a business owner exploring commercial solar solutions, or a policymaker shaping renewable energy policies, understanding the intricacies of solar-energy is essential for making informed decisions and driving positive change towards a sustainable energy future.
Conclusion :
It’s clear that the sun holds tremendous potential to revolutionize our world. From powering our homes and businesses to protecting the environment and fostering economic growth, solar-energy offers a path to a brighter, cleaner future for all. By harnessing the power of the sun and embracing innovative technologies, we can pave the way towards a more sustainable and resilient energy system. So let’s join together in the solar revolution, illuminating the path to a brighter tomorrow for generations to come.
Read More: Bbrainsgroups.com
FAQs
How do solar panels work?
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic cells within the panels absorb sunlight, generating direct current (DC) electricity.
What are the benefits of solar energy for homeowners?
Homeowners can benefit from solar energy by reducing their electricity bills, increasing property value, and contributing to environmental sustainability.
How much does a solar energy system cost?
The cost of a solar energy system depends on factors such as system size, location, and installation complexity. However, many homeowners can recoup their investment through energy savings over time.
Are there government incentives available for installing solar panels?
Yes, many governments offer incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and feed-in tariffs to encourage the adoption of solar energy.
What is net metering, and how does it work?
Net metering allows solar energy system owners to receive credit for excess electricity they generate and export to the grid, offsetting their electricity bills.
How long do solar panels last?
Solar panels typically come with warranties of 25 years or more and can last even longer with proper maintenance.
What is the environmental impact of solar energy production?
Solar energy production has minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuels, as it produces no greenhouse gas emissions and reduces dependence on finite resources.
Can solar panels work during cloudy days or at night?
While solar panels are most efficient in direct sunlight, they can still generate electricity on cloudy days and during daylight hours.
What factors should I consider before installing solar panels on my property?
Factors to consider include roof orientation, shading, local regulations, available incentives, and financial considerations.
How can I find a reputable solar energy installer?
Research local solar energy companies, read customer reviews, and ask for recommendations from friends or family members who have installed solar panels. Additionally, look for certifications and credentials from reputable industry organizations.
7 Responses