DC Charge Controller: Optimizing Solar Energy: Everything You Need to Know
Utilising Solar Energy: The Function of DC Charge Controllers
Envision harnessing the solar energy of the sun to efficiently and dependably supply power to your residence or commercial establishment. The central component of this procedure is the DC charge controller, an essential element that ensures the efficient operation of your solar power system. A DC charge controller is a device that regulates the flow of electric current from a direct current (DC) power source, such as a solar panel, to a battery. It plays a crucial role in preventing overcharging and over-discharging of the battery, which can lead to damage and reduced lifespan. Therefore, the DC charge controller is of utmost importance in maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of the battery.
A DC charge controller is a device that regulates the flow of electric current from a direct current (DC) power source, such as a solar panel or battery, to a DC load, such as a battery bank or electrical system. It ensures that the charging process is efficient and protects the batteries from overcharging or damage.
A DC charge controller serves as the central control unit of your solar power system. It regulates the transmission of electrical current from your solar panels to your batteries. It prevents overcharging, which can cause the batteries to become overheated and damaged, and also prevents excessive discharge, which can lead to accelerated wear and tear. In essence, it ensures that your batteries are consistently charged to an optimal level, enhancing their longevity and performance.
The Importance of a DC Charge Controller
Consider your solar power system as a highly efficient and smoothly functioning apparatus. In the absence of a charge controller, the system can become unregulated, resulting in issues and even hazardous situations. DC charge controllers are crucial for maintaining battery health and ensuring optimal functionality of your solar power system. They are an essential component for any solar power installation.
By comprehending the significance and function of DC charge controllers, you will realise how they enhance the efficiency of your solar power system. Continue reading to acquire comprehensive knowledge about these significant equipment and their ability to optimise the performance of your solar power system.
Notable Characteristics of Digital PWM Solar Charge Controllers
Adjustable Loading Timer: Allows you to precisely manage the timing of energy use for your devices, optimising usage during peak sunlight hours. The customisable loading timer enables you to establish certain time intervals for activating or deactivating the load, granting you enhanced authority over power use.
Timer with Adjustable Light Activation and Delayed Light Deactivation: Effortlessly conserve energy with the adaptable light timer, which allows you to establish a delay for automatically switching off lights after a specified period. This is ideal for illuminating outdoor spaces or any location where energy conservation is desired.
Automatic Detection for Batteries with Voltage Ratings of 12V and 24V: Simplify your setup with the use of auto-sensing technology. This function enables the controller to instantly identify whether your system utilises 12V or 24V batteries, simplifying the installation process.
Interface for LCD Display and Control: Stay updated with instantaneous data readily accessible. The LCD display provides crucial data such as battery voltage and charging current, while the user-friendly control interface facilitates effortless adjustments.
Temperature Compensation: Safeguard your batteries in any climatic conditions. Temperature compensation adjusts the charging parameters according to the battery’s temperature, ensuring optimal performance and longevity under varying environmental circumstances.
Specifications for PWM Solar Charge Controllers: Model Variants and Current Ratings
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Solar Charge Controllers: Available in several capacities, including 10 Amp, 20 Amp, 30 Amp, and 40 Amp variants, catering to varied system sizes. This enables you to select the most suitable option based on your specific requirements.
Electrical Voltage and Current Specifications: These controllers are compatible with both 12V and 24V systems and have load currents that are proportional to their size. This characteristic enables them to function effectively with a wide range of battery configurations.
Security Measures: Ensuring safety is crucial. These controllers are equipped with safeguards to prevent overload and short circuits, ensuring the safety of your system from electrical issues.
Metrics for Measuring Efficiency and Performance: Maximising efficiency is crucial for optimising the performance of your solar system. These controllers perform effectively with a no-load current of under 20 mA and a minimal voltage drop in the charging circuit.
Physical Dimensions and Design: These controllers are compact and practical, measuring around 6.5 x 4 x 1.5 inches. This size allows for easy installation without occupying a significant amount of room.
Categories of Solar Charge Controllers
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Controllers:
- Charging Method: PWM controllers maintain battery health by utilising power devices that alternate between on and off states.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: They have a low cost and straightforward design, however, they exhibit lower efficiency compared to MPPT controllers.
MPPT Controllers refer to Maximum Power Point Tracking controllers:
- Charging Method: MPPT controllers utilise maximum power point tracking to optimise the power output of solar panels by altering the input voltage.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: They exhibit high efficiency and flexibility, however, they come with a higher price tag and increased complexity.
Comparison: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) vs. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Controllers
Optimising the Use of Energy: Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers have the capability to extract an additional 30% of power from solar panels, particularly in varying weather circumstances, compared to Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controllers.
Price Comparison: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controllers are typically more cost-effective, rendering them suitable for smaller systems that have constrained budgets.
Compatibility of the System: MPPT controllers are specifically designed to be compatible with larger arrays and higher voltage systems, making them highly suitable for large-scale installations.
Effectiveness Under Varied Weather Conditions: MPPT controllers excel in cold and overcast conditions, ensuring optimal power extraction in situations where PWM controllers may struggle.
What are the Advantages of Using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) over Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)?
Economic Efficiency: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controllers are cost-effective, rendering them a favourable option for solar systems of modest to moderate scale.
Effortlessness and User-Friendliness: These products are straightforward to install and operate, making them ideal for individuals seeking a hassle-free setup.
Optimal Uses for PWM Controllers: Most suitable for modest residential systems or off-grid applications when the usage of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technology is not necessary.
What are the Advantages of Using MPPT over PWM?
Enhanced Energy Extraction: MPPT controllers optimise the energy output of your solar panels, resulting in significantly improved efficiency.
Versatility and Assistance for More Extensive Systems: Due to their ability to manage higher voltages and larger arrays, they are well-suited for large-scale applications.
Optimal Uses for MPPT Controllers: Well-suited for installations where maximising energy output is crucial, such as locations with fluctuating sunshine levels.
Installation and Configuration
Fundamental Installation Procedures:
- Install the Controller: Position the charge controller in close proximity to the battery bank, ensuring it is firmly secured.
- Establish the Battery Connection: Fasten the battery to the controller according to the provided wiring schematic.
- Establish the Connection of the Solar Panels: Establish the connection between the solar panels and the controller, ensuring that the connections are correct.
- Validate Connections: Inspect all connections to ensure they are secure and accurate.
- Activate: Switch on the controller and verify the configuration to ensure proper functionality.
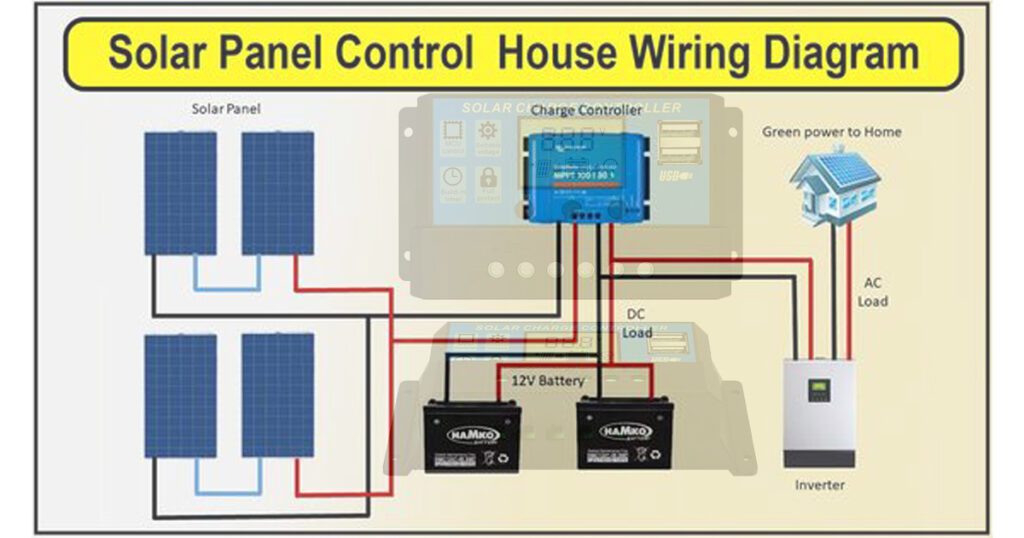
Schematic and Interconnections: Refer to the manufacturer’s wiring diagram to ensure accurate connection of all components, such as the solar panels, batteries, and load connections.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Common Installation Errors:
- Incorrect Polarity: It is essential to verify the polarity before making any connections.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all connections are properly fastened and firmly in place.
- Inadequate Ventilation: Place the controller in a location with proper airflow to prevent it from becoming too hot.
Repair and Problem-Solving
Tips for Regular Maintenance:
- Regular Inspections: Examine for any loose connections and indications of deterioration.
- Maintain Cleanliness: Regularly remove dust and ensure the controller remains free from any dirt or debris.
- Battery Maintenance: Routinely inspect battery condition and water levels (if necessary).
Common Problems and Resolutions:
- Overcharging: Verify the functionality of the temperature correction feature.
- Undercharging: Verify the solar panel’s electrical output and connections.
- Error Messages: Consult the handbook for troubleshooting instructions related to individual error codes.
When to Consider Seeking Professional Assistance?: If the controller exhibits chronic problems or intricate issues that cannot be readily resolved, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a professional installer or expert.
Factors to Take into Account for Safety
Electrical Safety:
- Effective Insulation: Ensure that all cables are properly insulated to prevent electric shocks.
- Prevent Water Damage: Place the controller in a dry location to avoid exposure to water.
Optimal Air Circulation:
- Thermal Management: Place the controller in a well-ventilated location to facilitate the dissipation of heat.
Proper Handling and Storage of Batteries:
- Secure Storage: Ensure that batteries are stored in a cool, dry location, shielded from direct sunlight and excessive heat.
- Safety Measures: Employ protective equipment when handling batteries to avert mishaps.
By adhering to this comprehensive guide, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of DC charge controllers and their indispensable role in solar power systems. Whether you are contemplating an upgrade to your current system or embarking on the installation of a fresh one, possessing this knowledge will enable you to make educated decisions and maximise the benefits of your solar power setup.
One Response